Blogpool, Hottub, Maintenance
Hot tub maintenance – Everything you need to know: Key terms and questions answered
Hot Tub Water Chemistry and Maintenance
Some questions you might have:
Explain the function of hot tub filters and explain why their maintenance is essential.
What is the recommended frequency for cleaning hot tub filters, and the procedures for weekly and monthly cleaning?
Explain the role of pH balance in hot tub water, explain the ideal pH range and the implications of an imbalance.
What are the main sanitiser options for hot tub water and what are the recommended residual levels for each?
Detail the procedure of draining and refilling a hot tub on a quarterly basis.
List five common contaminants that contribute to cloudy hot tub water.
Describe the process of “shock dosing” a hot tub, explaining its purpose and the different types of shock treatments available.
Besides shocking, what other measures can be taken to clear cloudy hot tub water?
What are the main reasons of foam in hot tub water and how to prevent them?
Explain the purpose of shocking a hot tub in relation to sanitizer effectiveness and the removal of chloramines or bromamines.
The answers to your questions
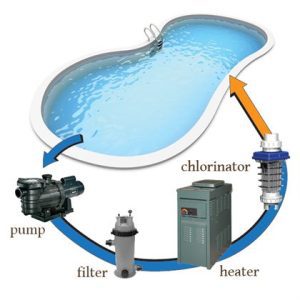
Hot tub filters capture and hold solid and particulate contaminants from the water to prevent water contamination. Proper maintenance will keep the filters effective at maintaining clear water, extending the life of the hot tub and ensuring that chemical treatment is as effective as possible.
Hot tub filters need to be cleaned once a week using a strong jet of water to remove debris. The monthly process involves soaking filters in a special cleaning solution to remove contaminants that have built up.
pH levels between 7.0 and 7.6 are required to ensure both bather comfort and effective sanitizing. An imbalance can cause skin irritation, damage to the equipment, scale formation, and reduced sanitiser efficiency.
The primary sanitizers are chlorine and bromine. The recommended residual levels for bromine are 2-4 mg/l, for inorganic chlorine are 2-4 mg/l, and for organic chlorine are 3-5 mg/l.
Draining and refilling every three months requires the use of a system flush to clean the pipes, a hose flush, shell cleaning, pipe and jet vacuuming, filling the tub with water via the filter area, and adding chlorine or bromine during filling.
The contaminants include environmental debris (dust, dirt, leaves), organic matter (dead skin, body oils), man-made organic contamination (cosmetics, detergents), heavy bather load and low sanitizer levels.
Shock dosing is the procedure of adding a strong oxidizing agent to eliminate organic pollutants and bring the sanitizer back to life. These include non-chlorine shock, chlorine granules, bromine granules and one-shot sachet treatments.
Other methods to clear the water include checking and adjusting the pH and sanitizer levels, cleaning or replacing the filters, and using a clarifier to bind small particles for filter removal.
Foam is caused by the accumulation of products and total dissolved solids (TDS) in the water, with jet action exacerbating this. Prevention measures include showering before use, rinsing bathing suits without detergent, using good quality chemicals, regular shock treatments, and leaving the cover off for aeration.
Shocking is necessary to destroy chloramines or bromamines, which are sanitiser by-products that decrease sanitiser effectiveness and produce incorrect readings on test strips. This means the sanitizer can kill bacteria and maintain safety of the water.
Useful terms
Sanitiser A chemical substance, such as chlorine or bromine, that kills or inactivates harmful microorganisms like bacteria and viruses in hot tub water.
pH A scale of the acidity or alkalinity of water from 0 to 14 with 7 as the middle and neutral point. The ideal pH of a hot tub is 7.0 to 7.6.
Total Alkalinity A measure of the water’s ability to resist changes in pH, acting as a buffer. Adequate alkalinity helps to maintain stable pH levels.
Shock Dosing The practice of adding a highly concentrated oxidiser to hot tub water to get rid of organic contaminants and bring back the effectiveness of the sanitiser.
Hot tubs and spas require routine chemical management for proper sanitizing of the water. Chloramines form through water treatment methods involving chlorine and ammonia or nitrogen-based substances. The chemical compounds limit chlorine effectiveness while producing irritating reactions.
The formation of bromamines results from bromine reactions with ammonia or nitrogenous compounds. Bromine effectiveness decreases when bromamines are formed while these compounds also create irritation issues.
Clarifier functions as a water additive that aggregates tiny water elements to create bigger particles which filters can easily capture thus improving water transparency.
Hot tub water passes through a physical barrier consisting of pleated fabric to remove solid debris and particulate matter which maintains water clarity and hygiene.
The TDS measurement shows the complete amount of dissolved substances present in water which includes minerals along with salts and organic matter. Water problems including foam and cloudiness emerge when TDS levels become excessively high.
The ratio between bathers and hot tub water volume determines both the rate of contaminant entry and the requirement for water maintenance procedures.
Biofilm represents a slimy microbial layer that forms on hot tub surfaces where bacteria can reside and negatively affect water quality.
An ozonator serves as a device that produces ozone to act as a strong oxidizer which helps sanitize hot tub water without needing chlorine or bromine.
UV Systems destroy hot tub water microorganisms using ultraviolet light as a secondary sanitizing method.
A system flush consists of a chemical solution which cleans hot tub plumbing to remove accumulated debris before the water needs draining and refilling.
Some products you might be interested in:
The recommended product selection includes